Polyfarmaci blandt ældre – orale aspekter
Denne kasuistik viser vigtigheden af at få håndteret orale sygdomstilstande forbundet med medicininduceret hyposalivation og ikke mindst betydningen af kontakt til patientens læge for en medicingennemgang/-sanering for mulig eliminering af årsagen.
Baggrund – Forekomsten af kroniske sygdomme, som kræver farmakologisk behandling, stiger med alderen. Ved en række sygdomme, herunder type 2-diabetes, iværksættes ofte behandlingsregimer bestående af en kombination af flere lægemidler (polyfarmaci). Mange ældre har flere kroniske sygdomme samtidigt (polymorbiditet), og de er derfor ofte multimedicinerede. Polyfarmaci øger risikoen for bivirkninger og interaktioner især hos ældre, hvor aldersbetingede ændringer i absorption, fordeling og elimination af lægemidler tillige øger risikoen for udvikling af lægemiddelinducerede helbredsproblemer, bl.a. xerostomi og nedsat spytsekretion.
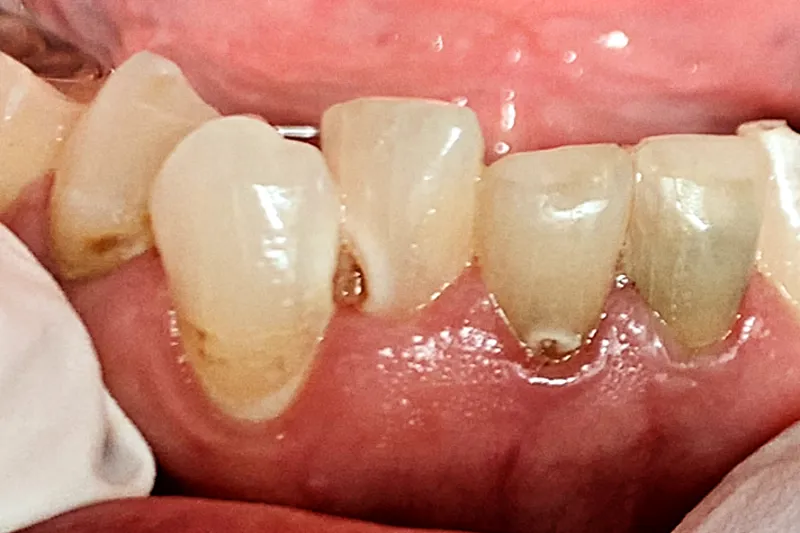
Patienttilfælde – Patienttilfældet omhandler en 69-årig kvinde, der får problemer med rygsmerter og herefter udvikler en række følgesygdomme, der fører til polyfarmaci. Sidstnævnte fører til udtalt xerostomi og hyposalivation, orale gener og sygdom, vægttab, social isolation, nedtrykthed, svækkelse og forringet livskvalitet.
Konklusion – Patienttilfældet viser vigtigheden af at få håndteret orale sygdomstilstande forbundet med medicininduceret hyposalivation og ikke mindst betydningen af kontakt til patientens læge for en medicingennemgang/-sanering for mulig eliminering af årsagen.
Klinisk relevans:
Polyfarmaci bliver stadigt mere udbredt. Polyfarmaci kan være tilsigtet og bero på en evidensbaseret ordination, fx ved behandling af type 2-diabetes. Polyfarmaci er dog forbundet med en øget risiko for at udvikle bivirkninger og lægemiddelinteraktioner især hos ældre, der ofte har flere sygdomme, som de bliver behandlet for samtidigt. Som tandlæge er det selvsagt vigtigt at have indsigt i patientens medicinforbrug i forbindelse med den odontologiske behandling, men også for at kunne vurdere, om patientens symptomer og eventuelle kliniske fund kan skyldes bivirkninger eller interaktioner relateret til patientens medicinforbrug, herunder polyfarmaci, og agere herpå ved at tage kontakt til patientens læge for medicingennemgang og mulig medicinsanering.Polypharmacy among elderly – oral aspects
Background – The incidence of chronic diseases that require pharmacological treatment increases with age. For a number of diseases, including type 2 diabetes, treatment regimens consisting of a combination of several drugs (polypharmacy) are often initiated. Many elderly people have several chronic diseases at the same time (polymorbidity), and therefore often take multiple medications. Polypharmacy increases the risk of side effects and interactions, especially in the elderly, where age-related changes in the absorption, distribution and elimination of drugs additionally increase the risk of developing drug-induced health problems, e.g. xerostomia and reduced saliva secretion.
Case study – This case describes a 69-year-old woman who develops problems with back pain and then develops a series of comorbidities that lead to polypharmacy. The latter results in pronounced xerostomia and hyposalivation, oral discomfort and disease, weight loss, social isolation, depression, weakness, and reduced quality of life.
Conclusion – This case study shows the importance of managing oral disease conditions associated with medication-induced hyposalivation, and not least the importance of contacting the patient's physician for a medication review/ deprescribing for possible elimination of the cause.


