Immunmodulerende behandling af maligne tumorer
Cancerimmunterapi aktiverer immunsystemet til at bekæmpe kræften, hvilket kan medføre markante behandlingsresultater, men også helt nye former for autoimmune bivirkninger. Immunregulerende antistoffer og cellulære immunterapier repræsenterer aktuelt de største kliniske gennembrud.
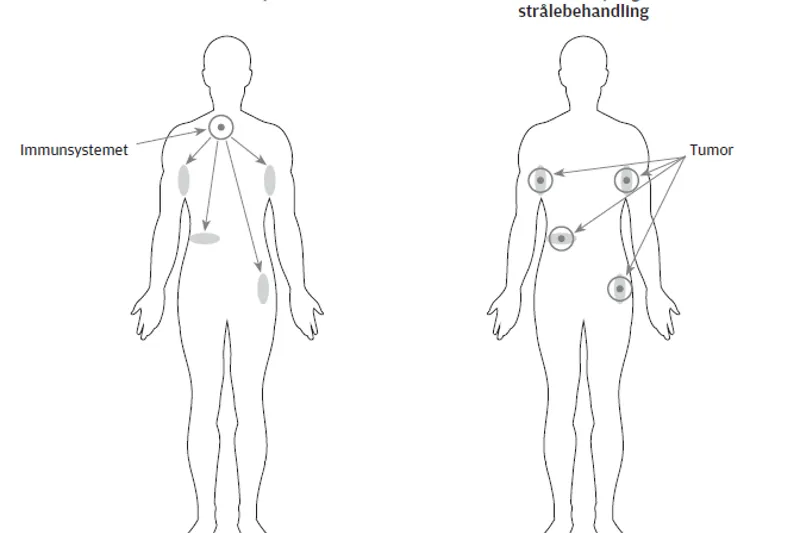
Immunterapi er en ny måde at tænke cancerbehandling på, hvor behandlingen er rettet mod immunsystemet og ikke direkte mod cancercellerne. Mange typer immunterapi såsom cytokiner, cancervacciner, cellulære immunterapier og antistoffer har været testet i kliniske forsøg gennem de seneste årtier.
Cancerimmunterapi aktiverer immunsystemet til at bekæmpe kræften, hvilket kan medføre markante behandlingsresultater, men også helt nye former for autoimmune bivirkninger. Immunregulerende antistoffer og cellulære immunterapier repræsenterer aktuelt de største kliniske gennembrud.
Klinisk relevans:
Det behandlingsmæssige landskab for metastatisk cancer har ændret sig markant indenfor de seneste få år. Introduktion af immunregulerende antistoffer har betydet bedre og ofte mindre bivirkningsfulde behandlinger til en række forskellige kræftformer. Immunterapien har dokumenteret klinisk effekt med chance for langtidsoverlevelse hos en undergruppe af patienter med metastatisk sygdom. Indikationsområdet for immunterapi udvides hastigt, ligesom kombinationsbehandlinger vinder frem. De bivirkninger, der kan forekomme under behandling med immunregulerende antistoffer, skyldes udløsning af autoimmune/inflammatoriske reaktioner. Disse bivirkninger kan være alvorlige, men kan oftest håndteres med immundæmpende midler.
Immune modulating therapy for treatment of cancer
Immunotherapy is a new modality in cancer treatment; a therapeutic strategy that targets the immune system of the cancer patient and not directly the cancer cells. Various types of immunotherapy such as cytokines, cancer vaccines, cellular immunotherapies and antibodies have been tested in clinical trials throughout the last decades. Cancer immunotherapy activates the immune system to attack cancer cells; this can lead to impressive clinical efficacy but also to new kinds of severe autoimmune side effects. Currently, immune regulatory antibodies and cellular immunotherapies represent the largest clinical break through.